Designed to Improve & Simplify Life While Being Distinctive for:
1. Enduring Quality
2. Renewable & High-Efficiency
3. Caring for the planet

Heat pump technology provides comfort
Heat pumps extract solar energy from the atmosphere to heat water. In this regard, they are comparable to solar water heating systems; the difference is that the energy required to heat water is extracted from the atmosphere rather than from direct sunlight.
This allows the heat pump to operate year round, regardless of weather conditions.
What advantages do you gain?

Reasons to appreciate your Buildings comforts

- Heat pump for your new construction
If you are constructing a new building today, you can compete in the premier league in terms of energy. A heat pump, like the one in the picture, is a constant source of comfort.
- Heat pump for your building improvement project
Even with a modernisation project, a heat pump heating system does not rely on limited resources.
Heat pump is beneficial in a variety of ways.
You get a future-proof heating system while lowering CO2 emissions. As a heat pump manufacturer, we aim to provide you with highly efficient appliances for hot water.
Your heat pump makes use of energy stored in the air. There are models suitable for every installation situation, whether it is a new build or a modernisation project; indoor or outdoor installation.
Why should you go with a heat pump?
Are you looking for a heating system that is environment friendly?
You won’t have to rely on fossil fuels if you use a heat pump as your heating system. This means you’ll be lowering your carbon footprint, which will benefit the environment.
Heat pumps convert stored energy in the air into heating energy. Not only that, but this heating method also ensures a consistent supply of domestic hot water. The air contains constant source of energy. Heat pumps are an important part of the energy transition.

Heat Pumps use solar energy to heat water by extracting it from the atmosphere
Heat Pumps are similar to solar water heating systems in this regard; the difference is that the energy required to heat water is extracted from the atmosphere rather than from direct sunlight. Ambient air has inherent heat at all temperatures above “Absolute Zero.” The technology used in heat pumps aids in harnessing this energy for productive purposes, with one key application being residential & commercial water heating.
The vapour compression cycle of refrigeration is the basis for how a heat pump works. The heat pump extracts heat from the atmosphere by passing air through an evaporator coil. The heat in the air aids in the vaporisation of an environment friendly refrigerant present in the evaporator. The refrigerant vapour is passed through a compressor, which significantly raises the refrigerant temperature. The hot gas is then moved around a heat exchanger, which also circulates water.
The refrigerant is routed through an expansion valve, where the pressure drops dramatically before being returned to the evaporator. The cycle is repeated until the water temperature reaches the desired level.
A heat pump can be compared to a refrigerator that works in the opposite direction.
Solar Energy is transferred from the atmosphere to heat the water, the input energy required is minimal. As a result, the resultant efficiency (COP) is very high.
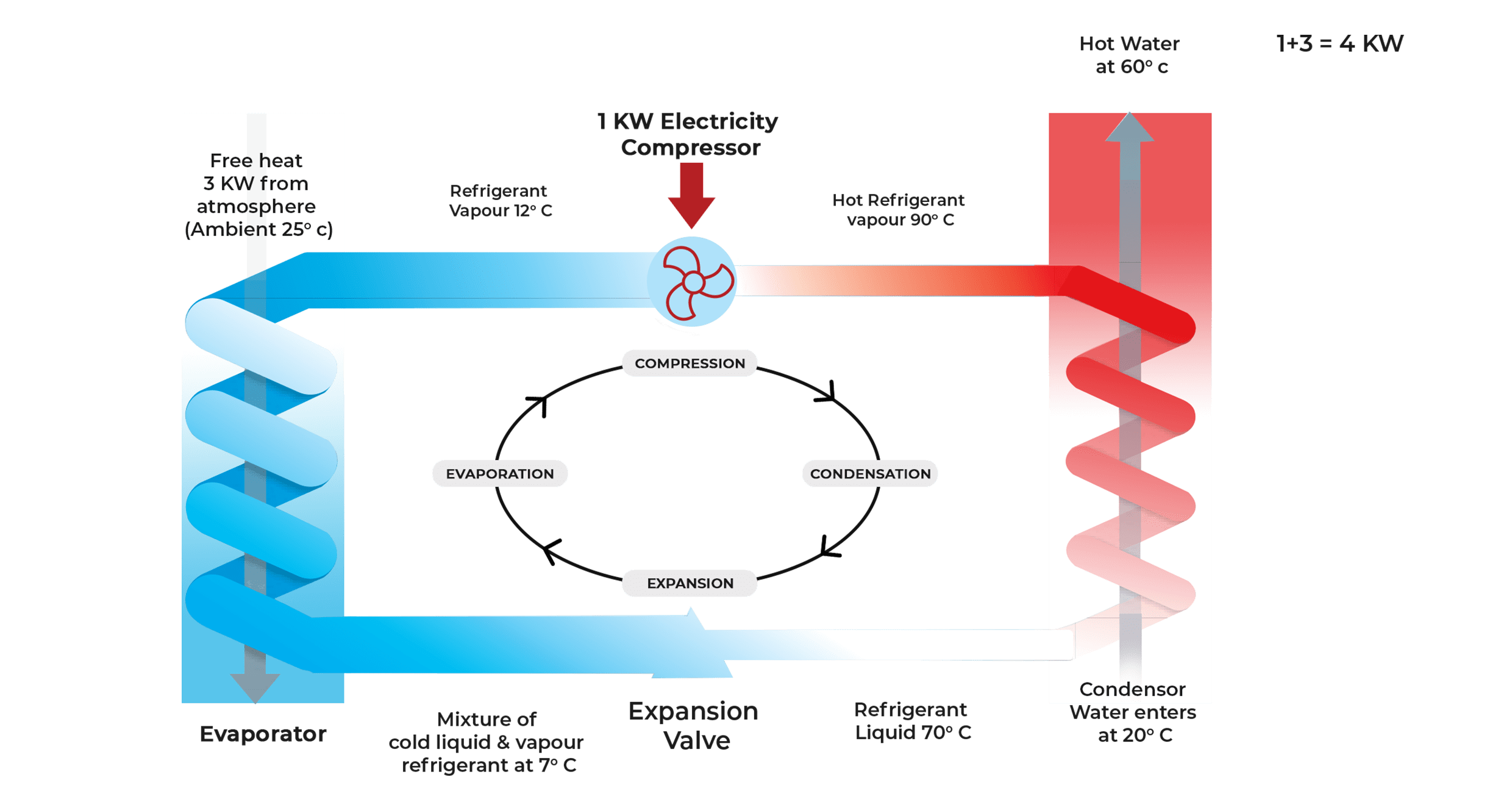
The diagram depicts a basic refrigeration cycle used in our heat pump water heaters. The system in your heat pump may be more complex depending on the unit you choose, but the basic principles apply. Heat energy is captured and transferred to the refrigerant flowing through the evaporator coil as air is drawn through the evaporator coil. The refrigerant, now a gas, is superheated hot gas as it passes through the compressor. This superheated gas now enters the condenser, where it transfers its heat energy to the domestic hot water via a double wall heat exchanger. The process is repeated as the superheated gas condenses back to a liquid.
A circulator pump constantly moves water from the storage tank through the condenser, raising the temperature of the water. Temperature rise and water flow rates differ depending on the configuration and conditions.
Energy efficient and environment friendly
According to the heat pump’s operating principles, for every unit of electric energy supplied to the machine, the machine is capable of delivering four units of heat energy to the water.
When compared to the efficiency levels of most traditional heating systems, heat pumps provide a novel approach to reducing the energy consumed in water heating.

Tips for Heat pump installation to save water:

Install the system as close to the point of use as possible to keep hot water pipe lengths to a minimum.

Ascertain that the heat pump is properly sized for the application.

For optimal flow rates, use energy-efficient shower heads.

Properly insulate the storage tank and hot water pipelines.

